Are Flat Feet More Likely to Cause Pronation?
Busting the Myth: Flat Feet Don’t Automatically Cause Pronation or Injury
Many people believe flat feet automatically lead to overpronation or injury, but this is a myth. Flat feet are often hyper-mobile, meaning they are naturally flexible rather than weak, and with proper activation and training, they can become strong, stable, and highly functional.
By engaging the foot muscles and strengthening the ankles, hips, and core, flat-footed individuals can control motion, reduce joint stress, and improve performance in running, walking, and other athletic activities.
Think of different foot types like eye colors—they’re natural variations, not defects. With the right exercises and training, every foot type can become strong, stable, and capable of supporting efficient, injury-free movement.
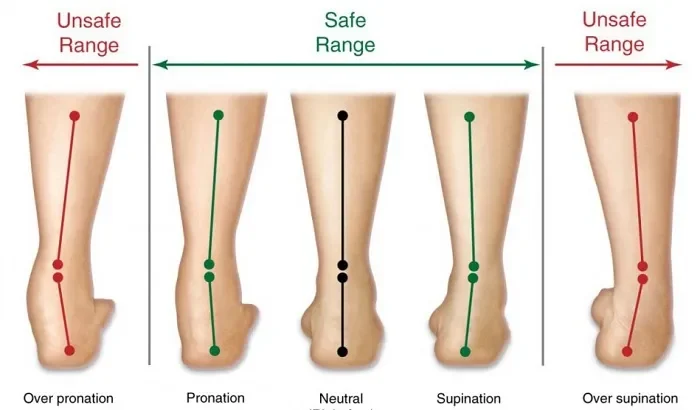
What is Pronation?
Pronation is the natural inward rolling of the foot that occurs when your heel strikes the ground during walking or running. It helps absorb shock, distribute weight, and adapt to different surfaces.
For people with flat feet, pronation often appears more pronounced because their arches are naturally lower or hyper-mobile. This can make it seem like the foot is “collapsing” inward, but in many cases, the foot is simply flexible rather than weak. With proper activation and strengthening of the foot, ankle, and hip muscles, flat-footed individuals can control pronation, maintain stability, and reduce stress on joints—debunking the myth that flat feet automatically lead to injury.
Credit: runtothefinish.com
Exercises for Flat Feet
Flat feet don’t just affect your feet. They can influence movement up the chain, including the ankles, knees, and hips, which all work together to manage pronation. Strengthening and stabilizing these areas is essential to control pronation, prevent injury, and improve overall performance.
Here are five exercises to help:
Arch Doming / Short Foot Exercise – Lift the arch without curling your toes to engage intrinsic foot muscles and improve arch stability.
Calf Raises - every time your heel comes off the ground the arch muscles light up with activity.
Toe Spread – there are muscles in the foot that contract to spread the toes apart. These muscles may weaken over time, and toe spreads help activate those muscles.
Single-Leg Balance / Hip Activation – Enhances ankle, knee, and hip control to manage pronation during movement.
Ankle Inversions / Eversions with Resistance Band – Builds lateral stability and strengthens supporting foot muscles to prevent excessive rolling of the foot.
Closing Out: Pronation and Flat Feet
Flat feet are often misunderstood, but with proper activation, strengthening, and mobility work, they can function just as effectively as any other foot type. By focusing on exercises that engage the arches, stabilize the ankles, and strengthen the hips, flat-footed individuals can control pronation, reduce stress on joints, and improve overall movement efficiency.
At Alpha Project Phyzio, we help runners and athletes manage flat feet and pronation to prevent injury and improve performance. Through targeted physical therapy for runners, foot activation, and strengthening exercises, we stabilize the lower body, improve gait mechanics, and optimize movement from feet to hips.